Abstract
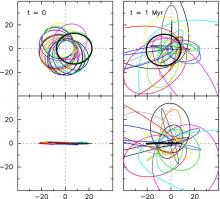
We study the short- and long-term effects of an intermediate mass black hole (IMBH) on the orbits of stars bound to the supermassive black hole (SMBH) at the center of the Milky Way. A regularized N-body code including post-Newtonian terms is used to carry out direct integrations of 19 stars in the S-star cluster for 10 Myr. The mass of the IMBH is assigned one of four values from 400 Msun to 4000 Msun, and its initial semi-major axis with respect to the SMBH is varied from 0.3-30 mpc, bracketing the radii at which inspiral of the IMBH is expected to stall. We consider two values for the eccentricity of the IMBH/SMBH binary, e=(0,0.7), and 12 values for the orientation of the binary's plane. Changes at the level of 1% in the orbital elements of the S-stars could occur in just a few years if the IMBH is sufficiently massive. On time scales of 1 Myr or longer, the IMBH efficiently randomizes the eccentricities and orbital inclinations of the S-stars. Kozai oscillations are observed when the IMBH lies well outside the orbits of the stars. Perturbations from the IMBH can eject stars from the cluster, producing hypervelocity stars, and can also scatter stars into the SMBH; stars with high initial eccentricities are most likely to be affected in both cases. The distribution of S-star orbital elements is significantly altered from its currently-observed form by IMBHs with masses greater than 1000 Msun if the IMBH/SMBH semi-major axis lies in the range 3-10 mpc. We use these results to further constrain the allowed parameters of an IMBH/SMBH binary at the Galactic center.