Abstract
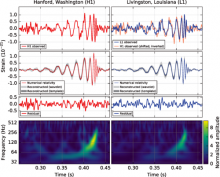
On September 14, 2015 at 09:50:45 UTC the two detectors of the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory simultaneously observed a transient gravitational-wave signal. The signal sweeps upwards in frequency from 35 to 250 Hz with a peak gravitational-wave strain of 1.0×10−21. It matches the waveform predicted by general relativity for the inspiral and merger of a pair of black holes and the ringdown of the resulting single black hole. The signal was observed with a matched-filter signal-to-noise ratio of 24 and a false alarm rate estimated to be less than 1 event per 203 000 years, equivalent to a significance greater than 5.1σ. The source lies at a luminosity distance of 410+160−180 Mpccorresponding to a redshift z=0.09+0.03−0.04. In the source frame, the initial black hole masses are 36+5−4M⊙ and 29+4−4M⊙, and the final black hole mass is 62+4−4M⊙, with 3.0+0.5−0.5M⊙c2 radiated in gravitational waves. All uncertainties define 90% credible intervals. These observations demonstrate the existence of binary stellar-mass black hole systems. This is the first direct detection of gravitational waves and the first observation of a binary black hole merger.