Abstract
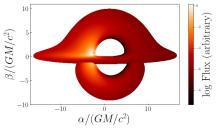
To reproduce the observed spectra and light curves originated in the neighbourhood of compact objects requires accurate relativistic ray-tracing codes. In this work, we present Skylight, a new numerical code for general-relativistic ray-tracing and radiative transfer in arbitrary space–time geometries and coordinate systems. The code is capable of producing images, spectra, and light curves from astrophysical models of compact objects as seen by distant observers. We incorporate two different schemes, namely Monte Carlo radiative transfer integrating geodesics from the astrophysical region to distant observers, and camera techniques with backwards integration from the observer to the emission region. The code is validated by successfully passing several test cases, among them: thin accretion discs and neutron stars hotspot emission.