Abstract
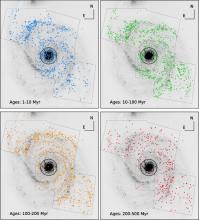
Recently acquired WFC3 UV (F275W and F336W) imaging mosaics under the Legacy Extragalactic UV Survey (LEGUS), combined with archival ACS data of M51, are used to study the young star cluster (YSC) population of this interacting system. Our newly extracted source catalogue contains 2834 cluster candidates, morphologically classified to be compact and uniform in colour, for which ages, masses and extinction are derived. In this first work we study the main properties of the YSC population of the whole galaxy, considering a mass-limited sample. Both luminosity and mass functions follow a power-law shape with slope −2, but at high luminosities and masses a dearth of sources is observed. The analysis of the mass function suggests that it is best fitted by a Schechter function with slope −2 and a truncation mass at 1.00 ± 0.12 × 105 M⊙. Through Monte Carlo simulations, we confirm this result and link the shape of the luminosity function to the presence of a truncation in the mass function. A mass limited age function analysis, between 10 and 200 Myr, suggests that the cluster population is undergoing only moderate disruption. We observe little variation in the shape of the mass function at masses above 1 × 104 M⊙ over this age range. The fraction of star formation happening in the form of bound clusters in M51 is ∼ 20 per cent in the age range 10–100 Myr and little variation is observed over the whole range from 1 to 200 Myr.