RIT Associate Professor Richard O’Shaughnessy contributes to study in 'Physical Review Letters'
Scott C. Noble
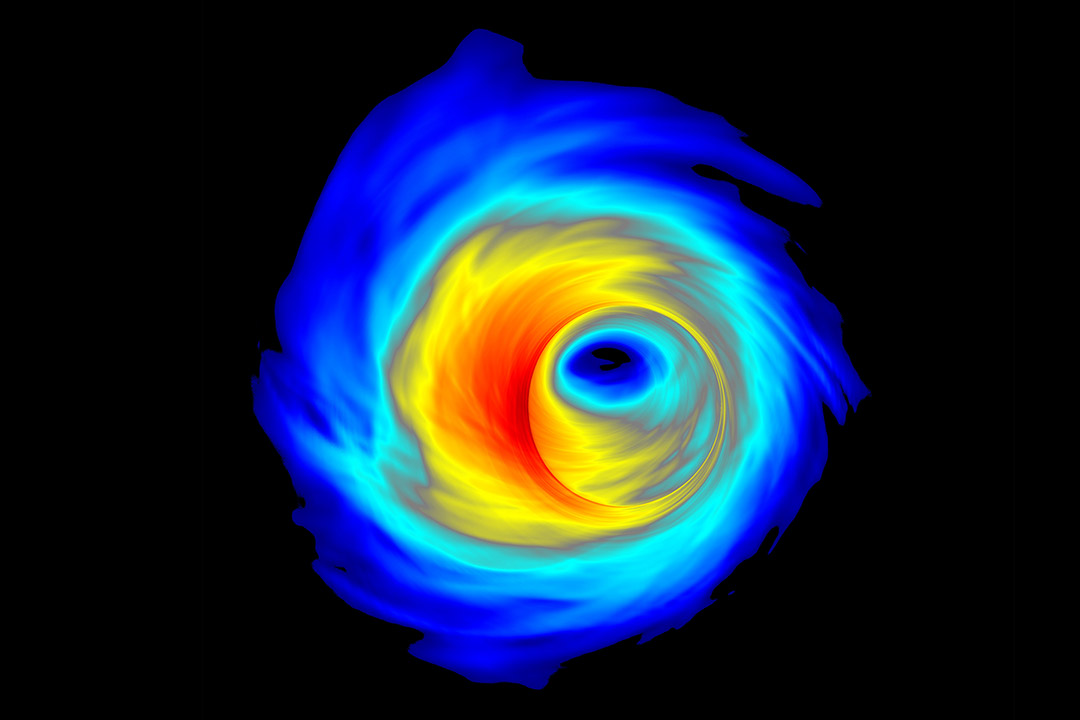
Simulation of an accretion disk surrounding a supermassive black hole.
Scientists have reported detecting gravitational waves from 10 black hole mergers to date, but they are still trying to explain the origins of those mergers. The largest merger detected so far seems to have defied previous models because it has a higher spin and mass than the range thought possible. A group of researchers, including Rochester Institute of Technology Assistant Professor Richard O’Shaughnessy, has created simulations that could explain how the merger happened.
In a new paper published in Physical Review Letters, the researchers suggest that such large mergers could happen just outside supermassive black holes at the center of active galactic nuclei. Gas, stars, dust and black holes become caught in a region surrounding supermassive black holes known as the accretion disk. The researchers suggest that as black holes circle around in the accretion disk, they eventually collide and merge to form a bigger black hole, which continues to devour smaller black holes, becoming increasingly large in what O’Shaughnessy calls “Pac-Man-like” behavior.
“This is a very tantalizing prospect for those of us who work in this field,” said O’Shaughnessy, a member of RIT’s Center for Computational Relativity and Gravitation (CCRG). “It offers a natural way to explain high mass, high spin binary black hole mergers and to produce binaries in parts of parameter space that the other models cannot populate. There is no way to get certain types of black holes out of these other formation channels.”
As the LIGO and Virgo collaboration continue to hunt for gravitational waves, O’Shaughnessy and his fellow researchers hope to find signatures of large, spinning black holes that could help confirm their models. If their assumptions are correct, it could help us better understand how the cosmic web of galaxies assembles.
“This could be a unique way of probing the physics around these supermassive black holes in a way that could not be probed in any other way,” said O’Shaughnessy. “It offers unique insight into how the centers of galaxies grow, which is, of course, essential to understanding how galaxies as a whole grow, which explains most of the structure in the universe.”
RIT’s CCRG has a large and active group of 18 faculty, students and postdoctoral researchers involved in the LIGO Scientific Collaboration. For more information, visit the CCRG website.